K8s study notes
Introduction
This is the second part of kubernetes study notes. History:
- From google Brog system
Resource
scope
- Namespace level
- eg: kubeadmin, k8s, kube-system
- Cluster level
- eg: role
- Metadata level
- eg: HPA
types
- workload
- Pod
- Deployment
- RC, RS
- DaemonSet
- Job / CronJob
- service discovery and loadbalance
- service
- ingress
- storage and configuration
- volume
- CSI
- special
- secret
- configMap
- downwardAPI : outside info into containers
Pod
Smallest resource in k8s
compulsory fields
- apiVersion ( string ): eg v1, app/v1
- kind ( string ): eg Pod, Deployment
- metadata ( object )
- name ( string )
- containers ( object[] )
- name ( string )
- image ( string )
important fields
- metadata
- namespace
- containers
- ImagePullPolicy
- IfNotPresent
- Never
- Always
- Ports
- Command
- WorkingDir
- ImagePullPolicy
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-pod
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Lifecycle
bc -> init Cs -> Main C ( start -> liveness ( readness ) -> stop )
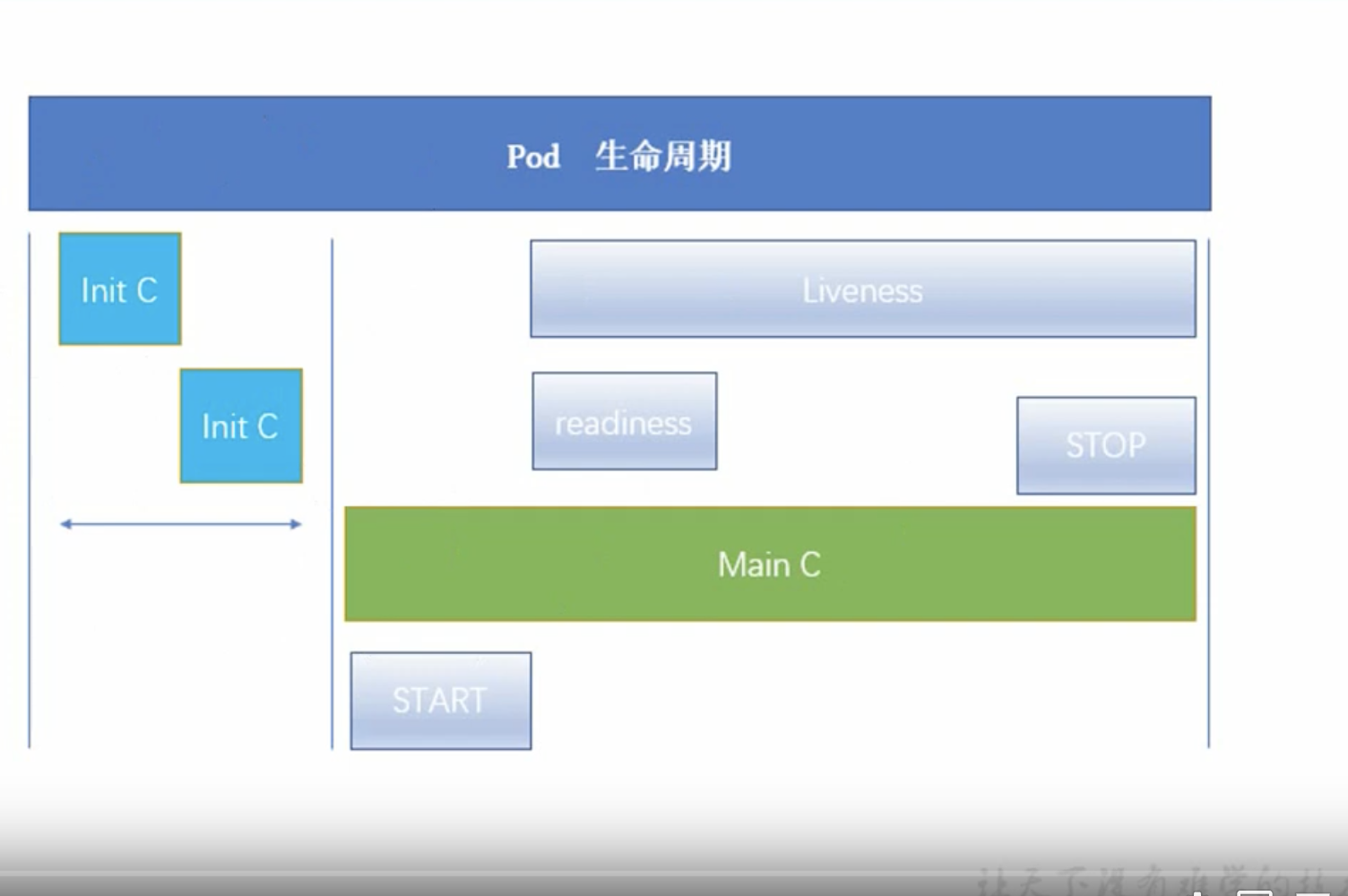
Init Container
- under linux namespace so can access resource which main container can not
- start one by one ( previous full stop ) after network and volume init ( basic container jobs )
- If fails, the Pod will fail
Main container Probe ( iterant )
- Actions
- ExecAction: exec command inside container
- TCPSocketAction: check ports open or not
- HTTPGetAction: check return code between 2xx and 3xx
- Types
- LivenessProbe: check container is running or not if fails Pod will fail
- ReadnessProbe: check service ready or not if fails all the services will delete the Pod ip
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-pod
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
readnessProbe:
httpGet:
port: 80
path: /index.html
initialDelaySeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 3
Status
- Pending: Pod Yaml been submitted to k8s. API objects been created and saved into etcd. But container not been created for some reason. eg: scheduler
- Running: Pod has been scheduled and bind to a node. All containers inside Pod are created and ready to service.
- Succeeded: All container inside Pod runs successfully, usually for one time job
- Failed: At least one container inside Pod fails
- Unknown: Pod stats not update by kubelet to api-server, usually means communication between master and nodes issue
Controller
Controller -> state machine
- ReplicationController And ReplicaSet
- Development
- DaemonSet
- StateFulSet
- Job / Cronjob
- Horizontal Pod Autoscaling
RC and RS
- RC -> RS
- RS support selector label
- maintain user defined replic number
Development
- support declarative statement ( apply ) to create Pod and RS, NB: Deployment -> RS -> Pods
- roll-update and rollback
- update -> create a new rs -> decrease old rs replic number and increase new rs replic number until old one replic number become zero
- rollback reverse process as update
- scale up and scale down
- pause and continue Deployment
create
kubectl apply -f xxx.yaml --record
scale
kubectl scale deployment nameOfDeployment --replicas 10
autoscale
kubectl autoscale nameOfDeployment --min 2 --max 15 --cpu-percent=80
update image
kubectl set image deployment/nameOfDeployment nginx=nginx:1.9.1
rollback
kubectl rollout undo deployment/nameOfDeployment
DaemonSet
ensure all ( some ) nodes have at lease one running
eg:
- storage:
cephglusterd - logs:
fluentdlogstash - monitor
collectdnew replicgmond
Job / CronJob
CronJob -> run a Job in certain time
CronJob spec
spec.scheduler- same as Cron min hour day month weekdayspec.jobTemplate- Job template
StateFulSet
- persistent storage
- persistent network identifiers
- deploy in order from 0 to n-1 and the previous pod must be ready and running
- delete in order from n-1 to 0
Horizontal Pod Autoscaling
Services
- With Label selector, match a group of pods to provide outside access.
- Only support 4 layers ( IP and port )of loadbalance not 7 layers, but with ingress can support 7 layers
Types
- ClusterIP (default): assign cluster internal ip ( restrict access within cluster ) to service
- NodePort: Bind a node port above Cluster IP to service for each node, port number > 30000
- LoadBalance: use cloud-provider add a loadbalance to NodePort( NodeIP:NodePort ), so it can be accessed outside cluster
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-svc
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- name: http
port: 8081
targetPort: 80
externalIPs:
- 192.168.99.102 # minikube IP, usually cloud provider
- ExternalName: import out-cluster service into cluster, so it can be access
Kube-proxy and VIP
Each node has kube-proxy running inside and will provide a virtual ip for each service. 1.1 iptables -> 1.14 ipvs
ipvs
- kube-proxy will regularly monitor
servicesandendpointsthen callnetlinkto create or update ipvs rules. - ipvs can provide multiple loadbalance algorithm
- rr - round robin
- lc - least connection
- dh - destination hash
- sh - source hash
- sed - least delay
- nq - not queued
- if install IPVS module will fallback to iptables
Ingress
ingress -> nodePort
https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/
configMap
kubectl create configmap nameOfconfigMap --from-file=PathToFile