Spring Study Notes
Basic Concepts
- Spring >= Container
- DI: dependency injection
- Bean
- application context: loads bean definitions and wires them together
- AOP: aspect- oriented programming
Spring modules
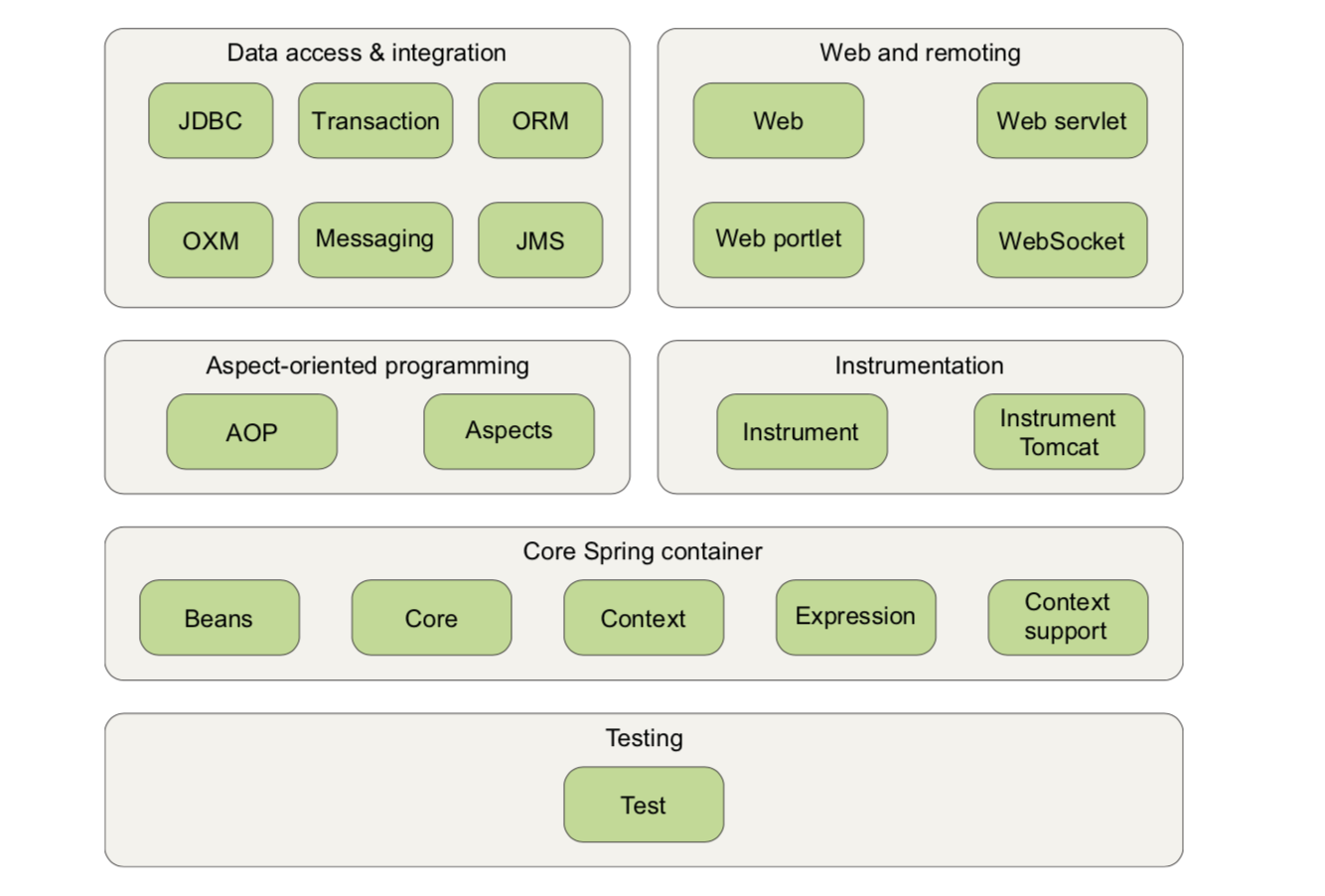
- CORE SPRING CONTAINER
- SPRING’S AOP MODULE
- DATA ACCESS AND INTEGRATION: abstracts away the boilerplate code
- WEB AND REMOTING: MVC and RMI
- INSTRUMENTATION : a weaving agent for Tomcat that transforms class files as they’re loaded by the classloader.
- TESTING
Beans
Spring beans vs Java beans
Spring beans POJO classes which develop as a part of spring Application is called Spring bean
java beans
- A class must be public and contain public default constructor.
- each private filed must contain either getter or setter or both method.
- A class can implement At most serializable or externalizable interface.
Configuration
- Explicit configuration in XML
- Explicit configuration in Java
- Implicit bean discovery and automatic wiring
- Component scanning—Spring automatically discovers beans to be created in the application context.
- Autowiring—Spring automatically satisfies bean dependencies.