ELF Format
ELF represents Executable and Linkable Format, which is a common standard file format for executable files, object code, shared libraries, and core dumps. It is a standard binary file format for *nix-like systems on x86 processors.
let us make a simple program
// hello.c
#include <stdlib.h>
char str[] = "Hello World\n";
int main (int argc, char** argv) {
printf("%s", str);
return 0;
}
Then compile it
gcc hello.c
Layout
A ELF file at least contains one ELF header and followed by file data:
- Program header table, describing zero or more memory segments
- Section header table, describing zero or more sections
- Data referred to by entries in the program header table or section header table

For example:
objdump -h a.out
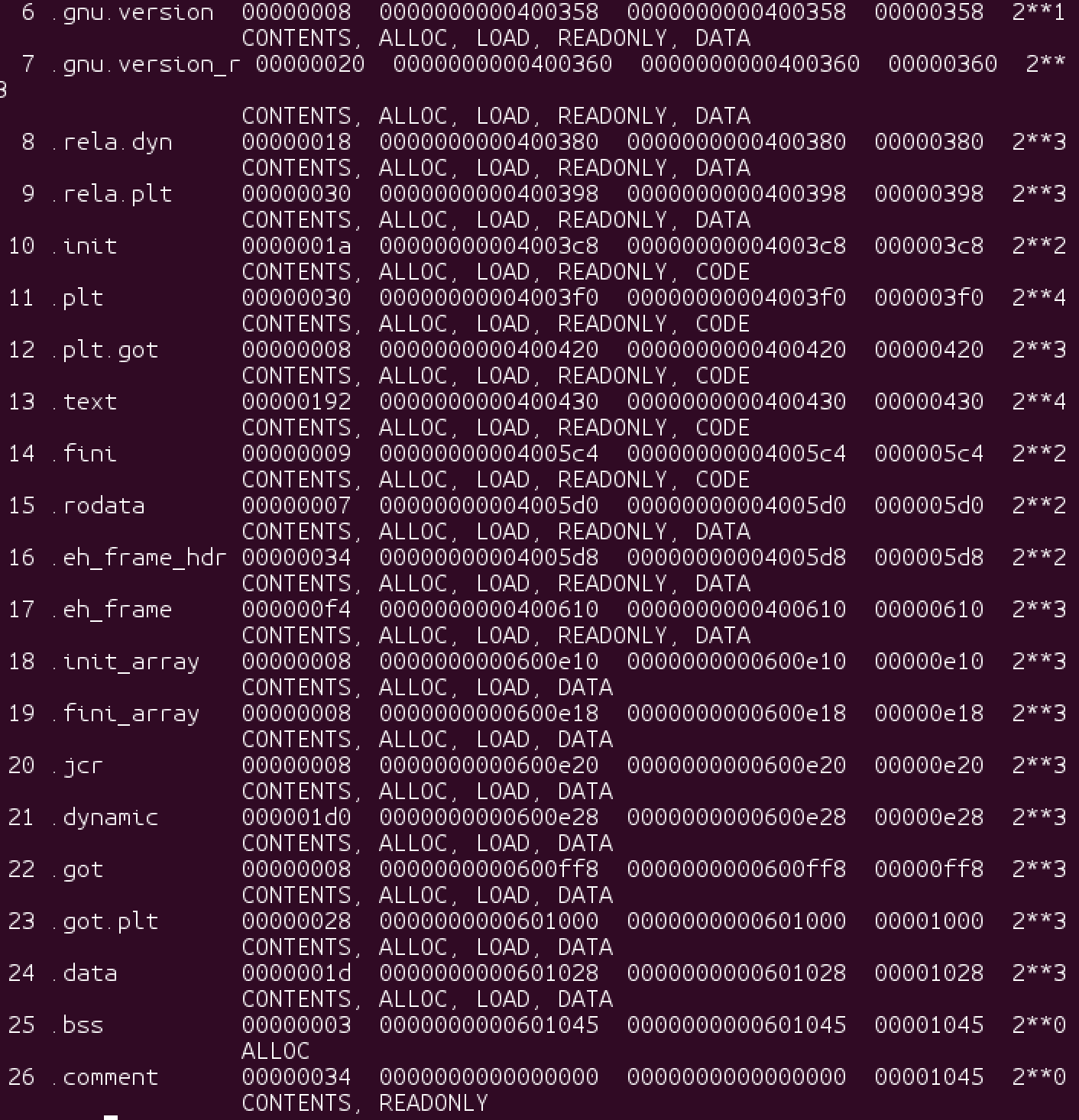
As can been seen above, a.out contains may section headers.
Section headers
Section headers table1
| Header Names | Meaning |
|---|---|
| .text | for codes |
| .data | for global tables, variables, etc |
| .bss | for uninitialized arrays and variable |
| .rodata | for strings |
| .comment & .note | just comments put there by the compiler/linker toolchain |
| .stab & .stabstr | debugging symbols & similar information. |
Reference
-
OSdev 2017, ELF, http://wiki.osdev.org/ELF ↩